
When current stops flowing through the coil, the internal contact returns to its initial state i.e. At that time the normally open (NO) terminal connects to the common (COM), and the normally closed (NC) terminal becomes disconnected. When current flows through the coil, the electromagnet becomes charged and moves the internal contacts of the switch. Between the remaining two pins (coil1 and coil2), there is a coil that acts like an electromagnet. While use of NC & NO terminals depends upon whether you want to turn the device ON or OFF. The mains electricity enters the relay at the common (COM) terminal. Typically the relay has 5 pins, three of them are high voltage terminals (NC, COM, and NO) that connect to the device you want to control. When a small current flows through the first circuit, it activates the electromagnet, which generates a magnetic field all around it. Initially the first circuit is switched off and no current flows through it until something (either a sensor or switch closing) turns it on. Here’s a simple animation illustrating how the relay uses one circuit to switch on another circuit. How Do Relays Work?Ī relay is an electromagnetic switch operated by a relatively small current that can control much larger current.
ARDUINO RELAY SHIELD TUTORIAL HOW TO
This tutorial walks you through how to setup the one channel relay module to switch on a lamp or other device, but let’s begin with a short introduction into relays. You can use a relay module to control the AC mains and Arduino to control the relay. But because the Arduino operates at 5 volts, it cannot directly control these higher voltage devices. Sometimes you want your Arduino to control AC powered devices like lamps, fans or other household devices. Getting started with the Single Channel 5V Relay Module (TONGLING) The over/under current and voltage protection of various ac and dc equipment.Electromagnetic relays are employed for the protection of various ac and dc equipment.Powered from external 5V or from male header.

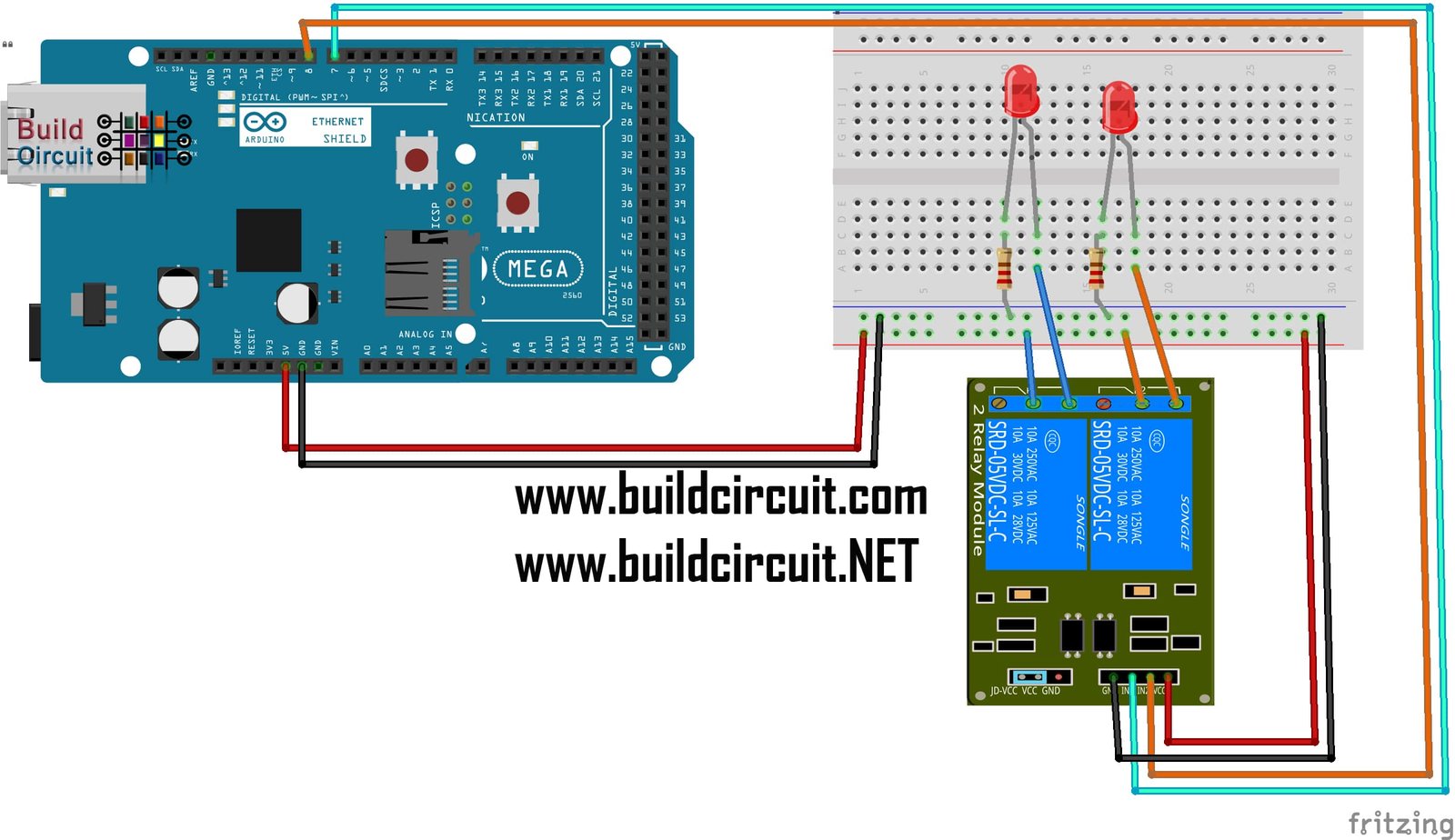
Each relay can switch variety of AC or DC high voltage, high current loads working at 110V or 220V AC mains like lights, fans, and motors and such. The board has one relay which works on 5V but the input signal can come directly from microcontroller output working at 3V or 5V to control relays.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
